What is the function of the esophagus in an earthworm?
Have you ever wondered about the intricate workings of earthworms, those fascinating creatures that dwell beneath the soil and silently contribute to the ecosystem? Among the many wonders of an earthworm’s anatomy, the esophagus holds a vital role that often goes unnoticed. In this article, we will delve into the function and significance of the esophagus in an earthworm, shedding light on its critical role in their survival and ecological impact.
What is the Esophagus?
Before we explore the function of the esophagus in an earthworm, it’s essential to understand what the esophagus actually is. The esophagus is a tubular organ that serves as a conduit for transporting food from the mouth to the digestive system. In earthworms, this tube-like structure plays a central role in their feeding process, facilitating the ingestion and processing of organic matter.
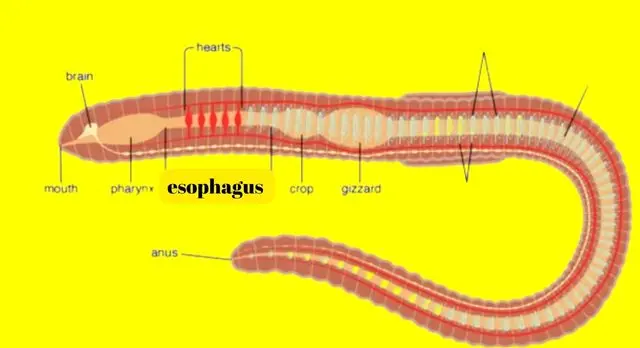
The Anatomy of the Earthworm’s Esophagus
The esophagus in an earthworm is a muscular tube lined with specialized cells that aid in the movement of food. It is located in the anterior part of the worm’s body, extending from the mouth to the crop, which is a temporary storage structure. The muscular walls of the esophagus contract and relax in a coordinated manner, creating peristaltic waves that push the food bolus towards the digestive system.
To better understand the anatomy, let’s take a closer look at the key components of the earthworm’s esophagus:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Prostomium | The upper lip-like structure that helps in food capture. |
| Pharynx | A muscular area that creates a sucking motion to draw in food. |
| Calciferous Glands | Secrete calcium carbonate to neutralize soil acidity. |
| Esophageal Gland | Produces mucus that aids in lubrication and digestion. |
The Function of the Esophagus in Feeding
The esophagus plays a pivotal role in the feeding process of an earthworm. As earthworms are detritivores, their primary diet consists of decomposed organic matter, such as dead plant material, fallen leaves, and other decaying debris present in the soil.
The feeding process of an earthworm can be broken down into the following steps:
- Food Capture: Earthworms use their prostomium, a sensory structure, to identify and locate organic matter in the soil. Once detected, the earthworm approaches the food source and prepares for ingestion.
- Ingestion: The pharynx, located at the beginning of the esophagus, creates a sucking motion, drawing in the organic matter into the esophagus.
- Neutralization of Soil Acidity: As the earthworm ingests soil along with the organic matter, it passes through the calciferous glands. These glands secrete calcium carbonate, which helps neutralize the acidity of the soil ingested with the food.
- Mucus Secretion: As the food travels through the esophagus, the esophageal gland produces mucus that coats the food bolus. This mucus aids in lubrication, making it easier for the food to move through the digestive tract.
- Peristaltic Movement: The muscular walls of the esophagus contract and relax in a coordinated manner, creating peristaltic waves. These waves propel the food bolus towards the crop, the first temporary storage structure in the digestive system.
The Role of the Esophagus in Digestion
While the esophagus is primarily responsible for transporting food, it also plays a minor role in digestion. Unlike humans and some other animals, earthworms lack specialized digestive enzymes in their saliva. Instead, digestion in earthworms primarily occurs in the intestine with the help of symbiotic bacteria.
However, the mucus secreted by the esophageal gland contains enzymes like amylase and lipase. These enzymes begin the process of breaking down complex carbohydrates and lipids in the ingested organic matter. As the food bolus moves through the digestive system, the intestinal digestive enzymes take over and further break down the food into absorbable nutrients.
The Importance of the Earthworm’s Feeding Habits
Earthworms play a crucial role in soil health and ecosystem functioning. Their feeding habits contribute to various ecological benefits:
- Nutrient Recycling: By consuming organic matter, earthworms aid in the breakdown of complex compounds into simpler forms, making essential nutrients more available to plants.
- Soil Aeration: Earthworms create burrows as they move through the soil, which enhances soil aeration and improves water infiltration. These benefits plant root growth and microbial activity.
- Organic Matter Decomposition: Earthworms accelerate the decomposition of organic matter, promoting the breakdown of dead plant material and enriching the soil with organic nutrients.
Key Takeaway
The esophagus of an earthworm serves as a crucial gateway to its digestive system, enabling the ingestion and processing of organic matter. This unassuming tubular structure plays a significant role in the earthworm’s feeding process, contributing to nutrient recycling, soil aeration, and organic matter decomposition. Understanding the function of the esophagus in an earthworm provides valuable insights into the intricate relationships between these humble creatures and the ecosystems they inhabit. So, the next time you encounter an earthworm, take a moment to appreciate the hidden marvel that is their esophagus and the remarkable contributions they make to the world beneath our feet.
What does the esophagus do in earthworms?
The esophagus in earthworms is like a tube that helps them eat and digest their food. It’s a passage that connects their mouth to their digestive system. When earthworms find food in the soil, they use their mouth to take it in, and the esophagus moves the food down into their stomach. The esophagus also releases some special juices that help break down the food and make it easier for them to digest.
What is the throat esophagus of the earthworm?
The “throat esophagus” is not a common term used for earthworms. However, it seems to refer to the pharynx, which is a part of the earthworm’s esophagus. The pharynx is a muscular area near the mouth of the earthworm. It helps the worm suck in the food it finds in the soil and pushes it down into the rest of the esophagus for digestion.
Where is the esophagus in an earthworm?
The esophagus in an earthworm is located in its body, connecting the mouth to the crop, which is a storage chamber in the digestive system.
What does the esophagus do in earthworms?
The esophagus in earthworms serves as a pathway for food. It helps transport the food they eat from their mouth to the crop, where it undergoes initial processing and softening.
What is the “throat esophagus” of the earthworm?
The term “throat esophagus” is not commonly used to describe any specific part of an earthworm. It is likely a reference to the esophagus itself, as it connects the mouth (throat) to the crop in the worm’s digestive system.
Related Post
